CONGENITAL SPINE PROBLEMS
Congenital spinal problems refer to congenital conditions that are caused by an abnormality in the development of the spine. These problems usually occur during the developmental stage of the fetus in the womb. Here are some of the congenital spinal problems:
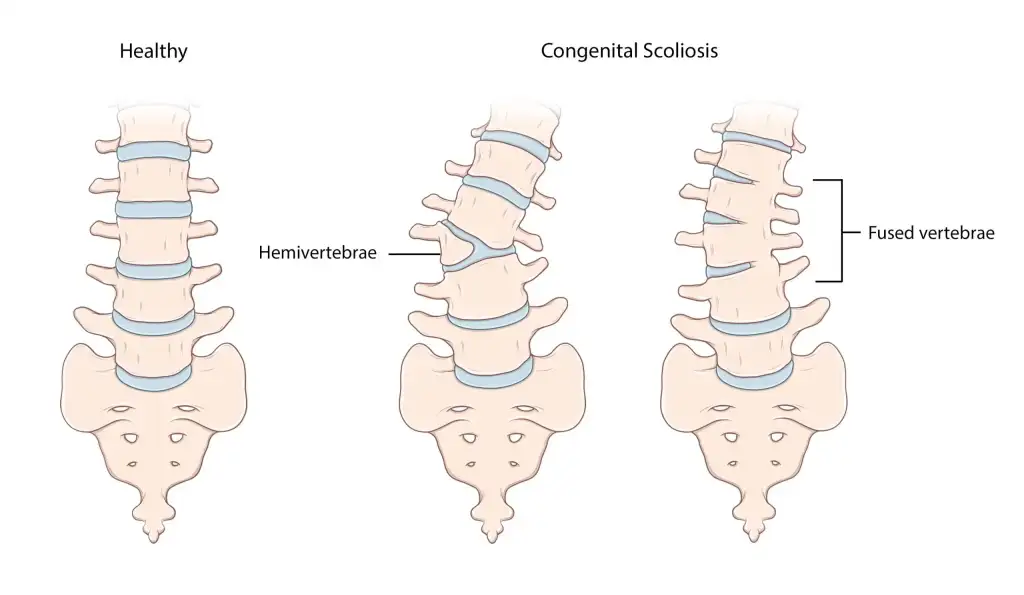
Hemivertebra:
Hemivertebra is a condition in which half of a vertebra does not develop. This means that the vertebra has a different shape than normal
Congenital Scoliosis:
Scoliosis is characterized by an abnormal curvature of the spine sideways. It usually begins in childhood or adolescence. The primary cause of this condition is usually unknown, but it may be associated with genetic factors and other congenital conditions.
Congenital Kyphosis:
Congenital kyphosis refers to a congenital curvature of the spine. The spine curves forward more than normal.
Sprengel Deformity:
Sprengel’s Deformity is a disease that occurs during the development of the baby in the womb, characterized by the shoulder blade (scapula) being higher than where it should normally be, leading to shoulder movement limitation and cosmetic problems.
Spinal Cord Anomalies:
Congenital abnormalities of the spinal cord include conditions associated with abnormal development of the membranes and fluid surrounding the spinal cord.
Costal Anomalies:
Costal anomalies refer to congenital abnormalities of the rib bones. These conditions usually affect the development of the spine and rib cage.
Spina Bifida:
Spina bifida refers to a condition in which the spinal cord fails to complete its normal development. An opening or crack forms between the spinal cord and the bones of the spine. This can lead to a number of problems that can affect the spinal cord.
These congenital spinal problems can cause a range of symptoms and complications, and treatment usually depends on the type and severity of the condition. In some cases, surgical intervention may be required, but in other cases, conservative treatment approaches can be used to improve the patient’s quality of life and manage symptoms. The treatment plan usually involves the involvement of a multidisciplinary team, usually consisting of orthopedic surgeons, physical therapists, neurologists and other specialists.
